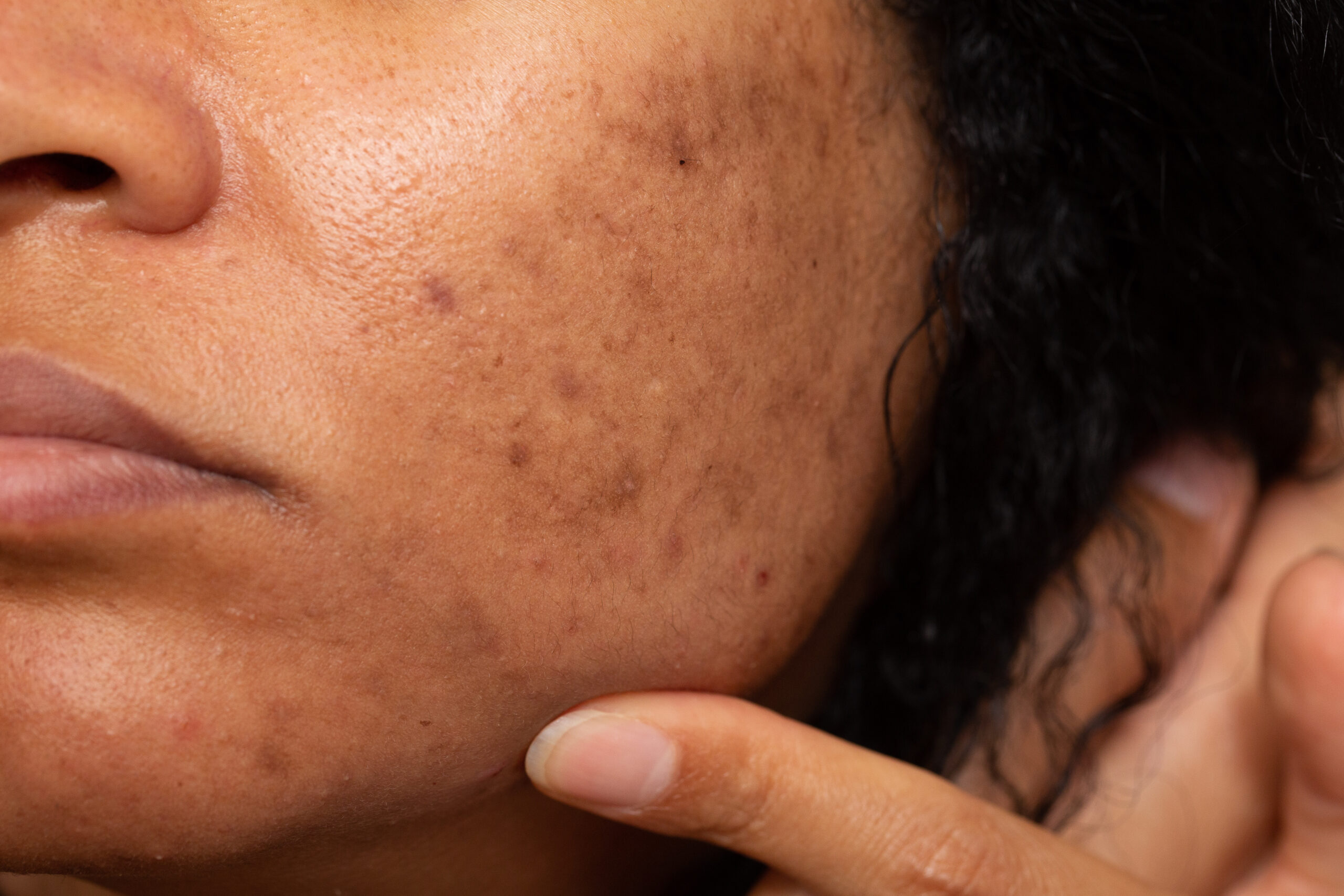
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation is the color of your skin. It comes from a natural pigment called melanin. Melanin is made by special cells in your skin. Sometimes, you may notice changes in your skin color. These changes are called skin pigmentation disorders. For example, you might see dark patches (hyperpigmentation) or light spots (hypopigmentation). Skin discoloration can affect anyone. However, it is more common in people with certain risk factors. Understanding skin pigmentation helps you care for your skin better.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Skin Pigmentation Changes
Skin pigmentation changes can look different for each person. But, there are some common signs to watch for. For instance, you may notice:
Sometimes, these changes may not cause pain or itching. Yet, they can affect how you feel about your skin.
Causes and Risk Factors
Many things can cause skin pigmentation changes. Some are common, while others are rare. Here are the main causes:
Additionally, people with darker skin tones may notice pigmentation changes more easily. Age can also play a role, as older adults often develop age spots.
Diagnosis Methods
If you notice skin discoloration, it is important to get the right diagnosis. Usually, a dermatologist will start with a clinical examination. They will look at your skin and ask about your health history. Sometimes, they may use a special light to see the spots better. In some cases, tests may be needed. For example:
Early diagnosis helps you get the best treatment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), seeing a skin specialist is important for proper care.
Treatment Options
Treating skin pigmentation depends on the cause. Some changes may fade on their own. However, others need medical help. Here are common treatment options:
Always follow dermatologist advice before starting any treatment. Some products may cause side effects if not used correctly.
Prevention Tips and Daily Skin Care Guidance
Although not all skin pigmentation changes can be prevented, you can lower your risk. Try these tips for healthy skin:
Moreover, check your skin often for new or changing spots. Early action can make a big difference.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
Sometimes, skin pigmentation changes may signal a serious problem. You should see a dermatologist if:
Remember, a dermatologist can give you expert advice and the right treatment plan.
Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on skin pigmentation concerns.