What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
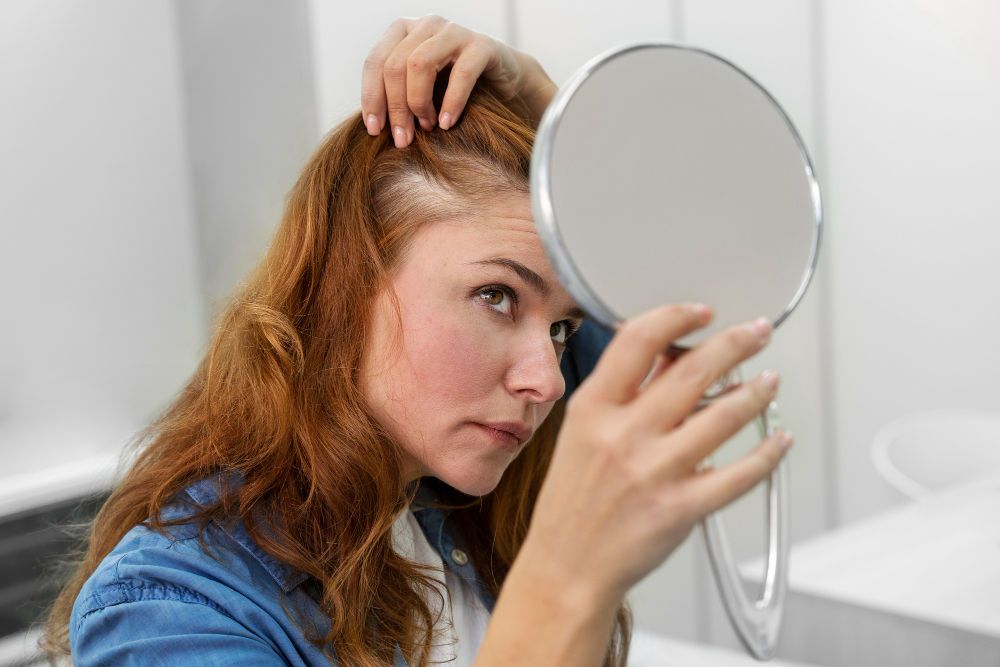
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition. It causes red, flaky, and itchy patches on the skin. Often, it affects the scalp, face, and other oily areas. Many people notice dandruff or scaly skin. Although it is not contagious, it can be bothersome. For some, seborrheic dermatitis comes and goes. Others may have symptoms for longer periods. Because it affects many people, understanding this condition is important.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Symptoms can vary from person to person. However, most people notice:
Sometimes, symptoms get worse in cold, dry weather. In babies, seborrheic dermatitis is called cradle cap. It appears as thick, yellow scales on the scalp. Adults may also notice symptoms around the nose, eyebrows, ears, or chest.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully known. However, several factors may play a role. For example, an overgrowth of a yeast called Malassezia can trigger symptoms. Also, oily skin and stress may make it worse. Some people have a higher risk, including:
Additionally, weather changes and harsh skin care products can trigger flare-ups. Although anyone can get seborrheic dermatitis, it is more common in adults aged 30 to 60 and in infants.
How Seborrheic Dermatitis is Diagnosed
Doctors usually diagnose seborrheic dermatitis by looking at your skin. They may ask about your symptoms and medical history. Sometimes, they gently scrape a small piece of skin to rule out other conditions. For example, psoriasis or eczema can look similar. Rarely, a skin biopsy is needed. Most of the time, no special tests are required. If you have ongoing or severe symptoms, seeing a dermatologist is helpful.
Treatment Options
Treatment helps control symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Many people find relief with simple steps. For mild cases, over-the-counter shampoos and creams can help. These may contain:
For more severe symptoms, doctors may prescribe stronger creams or shampoos. Sometimes, short-term use of mild steroid creams is needed. However, long-term use of steroids is not recommended. In addition, gentle skin care for seborrheic dermatitis is important. Always follow your doctor’s advice for best results.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While seborrheic dermatitis cannot always be prevented, some steps can help. For instance:
Additionally, try not to scratch affected areas. This can make symptoms worse. If you notice new or worsening symptoms, talk to your doctor.
When to See a Dermatologist
Sometimes, home care is not enough. You should see a dermatologist if:
Early treatment can help prevent complications. Moreover, a dermatologist can suggest the best plan for your skin type.
In summary, seborrheic dermatitis is a common but manageable skin condition. With the right care, most people can control their symptoms. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on seborrheic dermatitis.